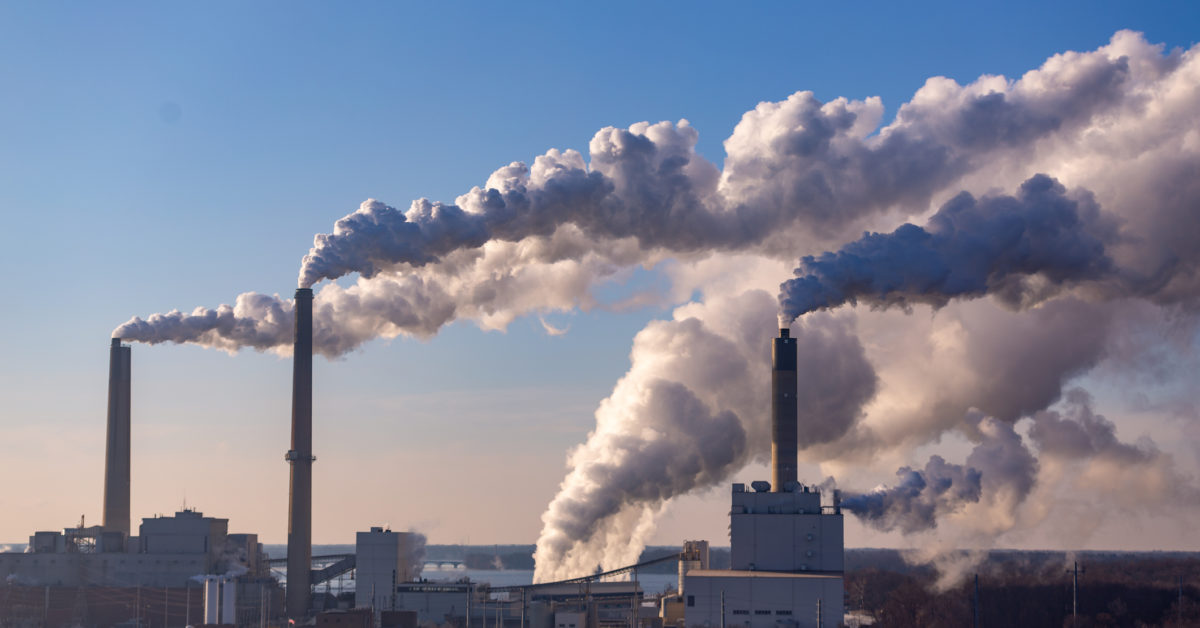
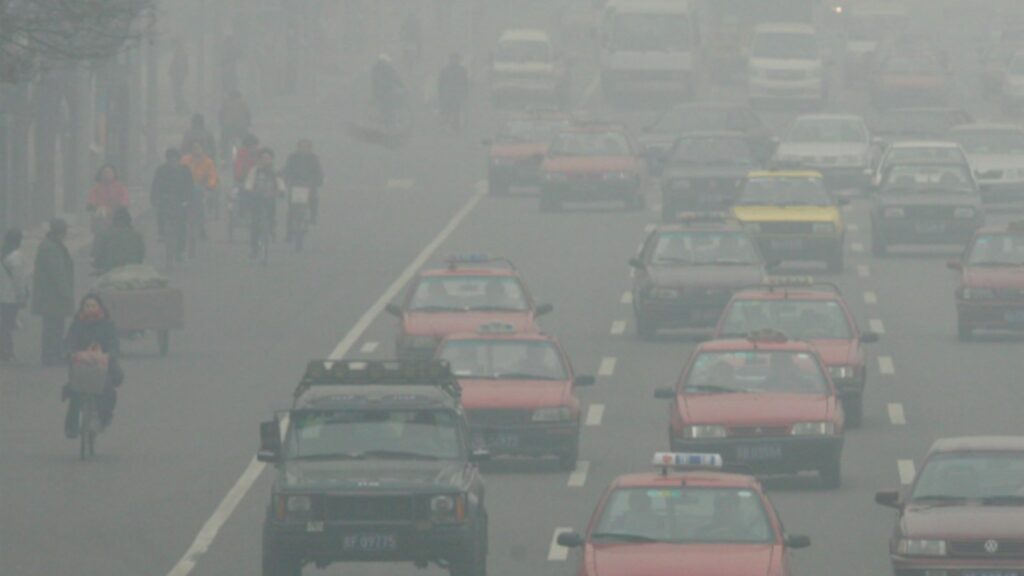
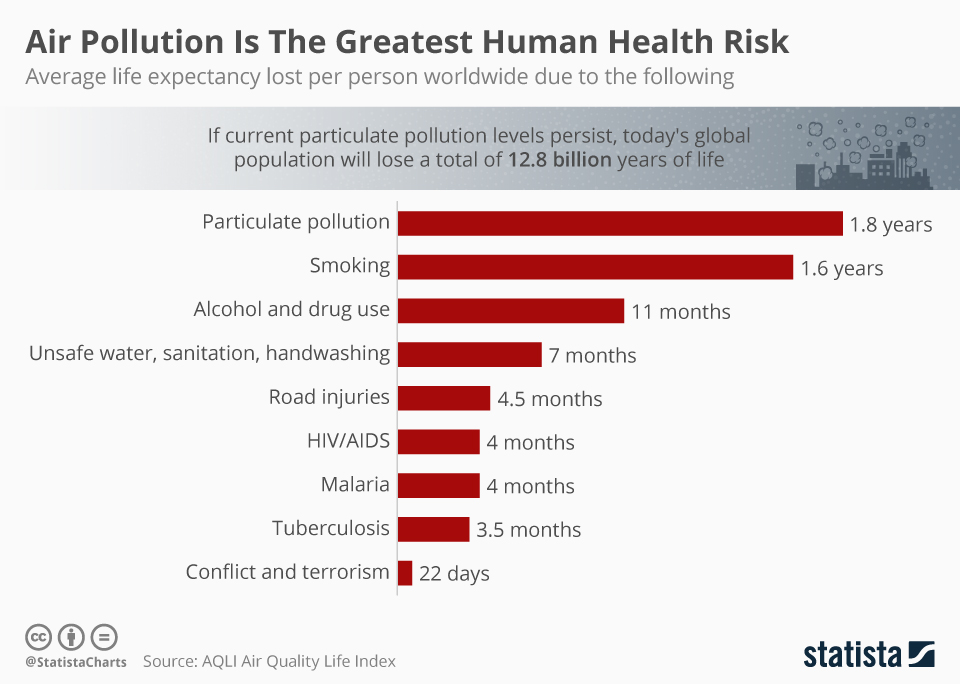
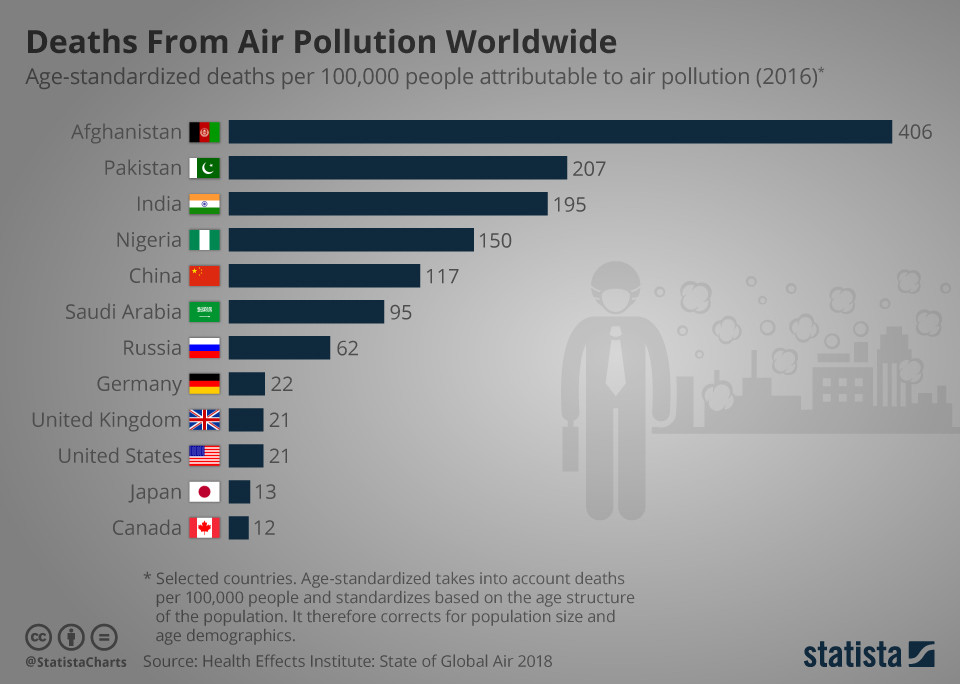
Air pollution is the release of both man-made and natural pollutants that cause negative effects on humans and the planet as a whole. These pollutants can take shape as solid particles, liquid droplets, or gaseous chemicals and present themselves in many different forms like carbon monoxide from car emissions or toxic, airborne chemicals from fires. Exposure to large amounts of air pollution for a prolonged period of time can cause many health problems for people of all ages, and the issue is only becoming worse.
Natural Air Pollutants
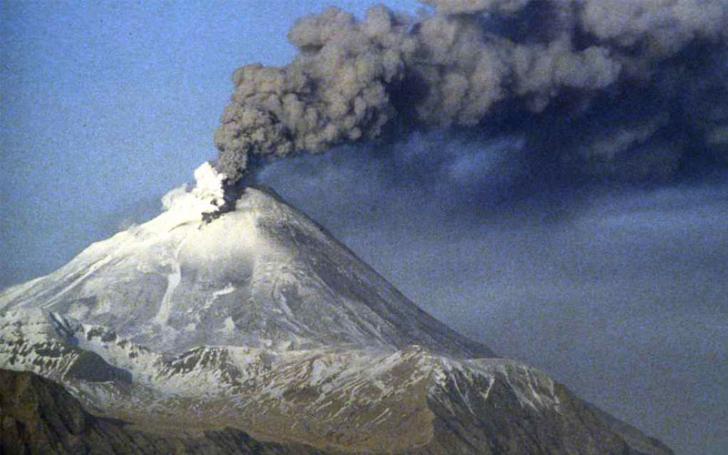

Air pollutants can occur naturally from volcanoes and wildfires in the form of smoke and ashes, both of which release chemicals that cause respiratory problems. Other forms of natural air pollution include allergens like pollen, which can cause mild symptoms like sneezing, and mold, which can cause severe health issues like lung infections.
In addition, one chemical called ozone naturally occurs in the upper atmosphere to protect the earth from the sun’s UV rays, but at ground level, the molecule is a pollutant that can harm plants and cause smog.
Man Made Pollutants
Although natural air pollutants make up a percentage of air pollution, the majority of air pollutants nowadays are caused by humans. Chemicals like sulfur dioxide, nitrogen dioxide, and carbon monoxide are emitted from burning fossil fuels in power plants and automobiles and released into the air. Waste burning also releases dangerous metals like mercury and makes up 29% of toxic, lung-affecting particles called PM 2.5. Furthermore, these particles can mix with weather conditions and create a major form of air pollution called smog.

Photochemical smog, often found in warm cities, is created when sunlight reacts with nitrogen dioxide, which comes from motor vehicles, and volatile organic compounds (VOCs), which come from paints and petroleum usage. The sun exposure then further breaks down the chemicals into secondary pollutants like ground level ozone.
In addition, the accumulation of sulfur oxides from sulfur-bearing fossil fuels like coal can accumulate in industrial cities and cause industrial/sulfurous smog and respiratory issues. The increase in sulfur dioxide also contributes to the formation of acid rain which damages wildlife and infrastructure.
When these large mixtures of harmful chemicals combine with the surrounding environment, it can create toxic photochemical and industrial smog which is detrimental to the health of both humans and the environment.
Effects On Health
Air pollution has been found to affect people of all ages, globally. Since these toxic chemicals are in a gaseous form, winds can spread the compounds over large areas, affecting more than just people living in urban areas with smog.
Day to day exposure to the sulfur oxides and nitrous oxides in smog can cause eye, nose, throat, and lung irritation for the short term. However, exposure to fine particulate matter (PM2.5), microscopic toxic particles in air pollution, pose the greatest risk to human health. This particulate matter is small enough to enter the bloodstream after inhalation and create serious, long term health problems. Once in the bloodstream, the particles can induce inflammation, causing an exacerbation of asthma, heart attacks, lung cancer, and strokes, especially in people over 60.
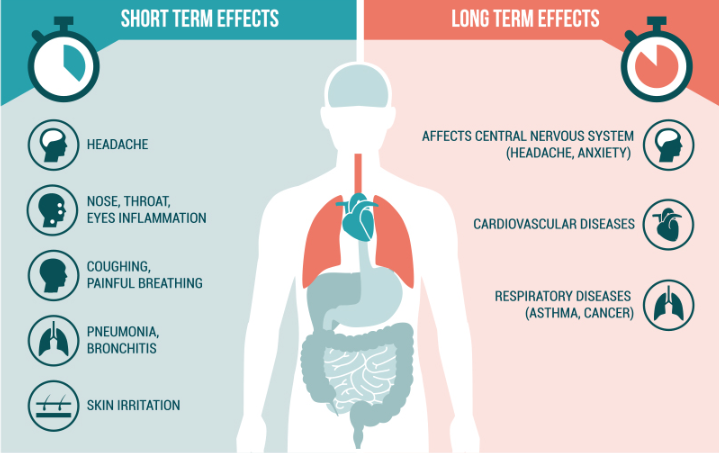
Since the matter can enter the bloodstream, it can affect all major organs, including the brain. According to María Neira, a public health expert at WHO, these pollutants can cause birth defects and disabilities in prenatal children and inhibit brain development and cognition in young children. In addition, pollutants can cause brain inflammation and declining brain function in adults. Some studies even found that the increased brain inflammation and plaque build up can cause degenerative brain diseases like Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s.
According to the World Health Organization, there are “seven million premature deaths a year caused by exposure to the bad quality of the air we breathe.” That’s more than the population of Finland wiped out each year. Air pollution is a serious, global issue that affects everyone.
Solutions
The key solution to fighting air pollution is reducing harmful emissions by improving fuel efficiency, using renewable energy sources, and investing in public transport. These solutions would lessen the amount of carbon being released and in turn reduce smog and other forms of air pollution. Cities like Los Angeles and Beijing have already recognized this and have implemented similar policies to combat air pollution.
For example, Los Angeles has made steps to expand and improve public transportation through technology, in an effort to increase public transit. Increased public transportation would help reduce the number of motor vehicles in use and therefore the number of emissions being produced. The city has invested in new, electric public transit that would eliminate emissions altogether. In July 2020, Metro deployed its first zero emission electric bus in Los Angeles with the entire Metro bus fleet projecting to be completely electric by 2030.

In the capital of China, where coal is the single-largest energy source and source of air pollutants, the State Council enacted the Air Pollution Prevention and Control Action Plan (2013) and has been investing in ways to reduce emissions and eliminate air pollution in Beijing and the surrounding areas. To meet the Action Plan, coal companies have found ways to reduce coal consumption and increase energy efficiency. For example, Wangping Power Company has installed heat recovery units and a heat pipeline to collect the waste heat from electrical production and transfer the energy to heat homes. According to the World Bank, a financial supporter of the project, “This has led to the elimination of 10 small polluting coal boilers that used to supply residential heating, reducing emissions of CO2 by 420,000 tons, nitrogen oxide [LP1] by over 6,330 tons and sulphur dioxide SO2 by over 13,100 tons annually.” With the improvement of technology, companies now have many ways to increase their fuel efficiency and reduce air pollution.